Disaggregated Prefill-Decode: The Architecture Behind Meta's LLM Serving
Why I'm Writing This Series
I've been deep in research mode lately, studying how to optimize LLM inference. The goal is to eventually integrate these techniques into JarvisLabs - making it easier for our users to serve models efficiently without having to become infrastructure experts themselves.
As I learn, I want to share what I find. This series is part research notes, part explainer. If you're trying to understand LLM serving optimization, hopefully my journey saves you some time.
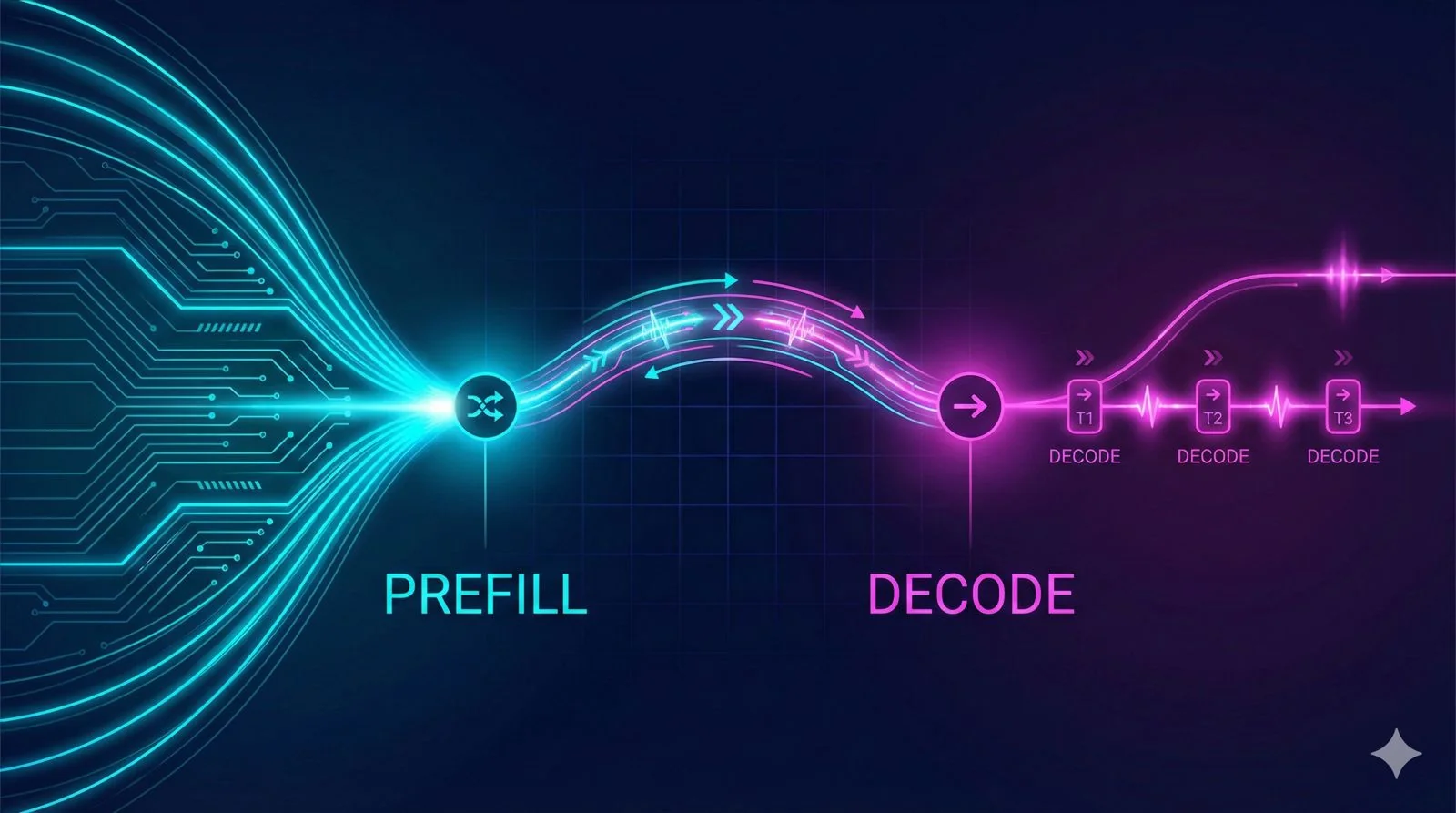
This first post covers disaggregated prefill-decode - a pattern I discovered while reading through the vLLM router repository. Meta's team has been working closely with vLLM on this, and it solves a fundamental problem that's been on my mind.